SMITH’s FRACTURE
SMITH’s FRACTURE
INTRODUCTION:
Smith’s Fractures is also known
as a Goyrand Fracture in French literature. Smith’s fracture is palmarly
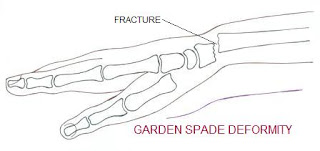
displaced distal radius fracture. It is referred to as “GARDEN SPADE”
deformity. Smith’s fracture is a reversed Colle's fracture.
ANATOMY:
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
Smith’s fracture
account for less than 3% of all fractures of the radius and ulna and have a bi-modal distribution: young males (most common) and elderly females.
MECHANISM:
Smith’s fractures usually occur
in one of the 2 ways:
Ø
a
fall onto a flexed wrist
Ø
direct
blow to the back of the wrist
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS:
Ø
Typically
acute pain in the wrist from an impact or a fall.
Ø
Tenderness
in the affected area.
Ø
Pain
is felt while moving the wrist.
Ø
Development
of swelling.
Ø
Wrist
may become deformed.
Ø
Appearance
of hand being downwards.
Ø
Fractured site may develop a cracking noise.
Ø
Symptoms
of fever few hours after injury.
CLASSIFICATION:
SMITH’S FRACTURE can be broadly
be classified into two types.
·
NONDISPLACED
FRACTURE: This
is frequently called as mild fracture. The treatment for this condition is casting.
Once the problem is diagnosed immediate attention must be given. The area of
the fracture gets healed in few weeks.
·
DISPLACED
FRACTURE: This
type of fracture is very severe in nature. Displaced generally leads to very
serious and dangerous damage to the bone. In this condition the joint of the
wrist is often displaced forward creating discomfort over the wrist while moving
in some angles.
Types of SMITH’S FRACTURE
classified based on the type of injury.
INVESTIGATION:
Ø
X-ray
of the wrist.
Ø
CT
is advisable in Comminuted type of fracture
Ø
MRI
in rare cases.
TREATMENT:
Smith’s Fractures can be
treated with manipulation and reduction.
v NONSURGICAL TREATMENT: Conservatives measures involve
closed reduction with use of local anesthesia and then casting of hand to
thumb. It takes about 10 weeks for complete recovery, which involves period of
immobilization(casting/slab) for about a month and then splinting for 6 weeks.
v SURGICAL TREATMENT: Surgery is needed in majority of
cases with Smiths Fracture as the deformity cannot be treated with nonsurgical
means. This method is termed as OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION(ORIF).
This is done by creating an
incision for interpretation of fracture and to get it back to its normal place.
This at times requires pins, screws, etc for fixation.
PHYSIOTHERAPY:
This is essential for everyone
for appropriate healing and normalizes function of wrist and hand can include:
·
Joint
mobilization.
·
Soft
tissue massages.
·
Ice
and heat.
·
Therapy
focusing on improving the strength.
·
Activity
modifications.
·
Attempts
at returning to activity.
--The End--







Comments
Post a Comment
Thank you for your kind words and your support.